Undergraduate Program
Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm-D)
Quick Link
Introduction
The Pharm.D. program at Salim Habib University prepares students for diverse roles in clinical, industrial, and entrepreneurial pharmacy through evidence-based learning and hands-on training. Our curriculum emphasizes the development of professional, ethical, and community-centered healthcare services.
With a strategic vision to strengthen academic excellence, students benefit from specialized departments, advanced laboratories, and industry-aligned sessions and interdisciplinary projects to foster innovation.
Pharm.D. is a five-year degree program focusing on pharmaceutics, pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmacognosy, basic medical sciences and pharmacy practice. Our state-of-the-art facilities, including simulation labs and industry-grade equipment, offer real-world exposure and skill enhancement. Work placements further enrich the learning experience, bridging academic knowledge with professional application.
Become part of a dynamic and future-focused program that equips you to lead in global healthcare and pharmaceutical industries.
About Program
Program Objectives
- Develop a strong foundation in pharmaceutical, clinical, and biomedical sciences.
- Equip students with skills for patient-centered care and evidence-based decision-making.
- Prepare graduates for diverse roles in community, hospital, and industrial pharmacy settings.
- Promote ethical responsibility, professionalism, and lifelong learning in pharmacy practice.
- Encourage innovation and entrepreneurship in pharmaceutical sciences.
- Train students to design and conduct research relevant to public health and drug development.
- Develop effective communication, leadership, and teamwork skills.
- Foster critical thinking and problem-solving abilities for clinical and industrial applications.
- Support preparation for national and international pharmacy licensing examinations.
- Build capacity for collaboration with healthcare professionals to optimize patient outcomes.
Internship and Career Prospects
1. Industry
Pharmaceutical industry offers a wide range of career prospects for pharmacists, combining their expertise in medication with opportunities for innovation and patient care. Pharmacists in this field can work in various roles, including:
- Research and Development (R&D): Pharmacists contribute to the discovery and development of new drugs, conducting experiments and clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Quality Control and Assurance: Ensuring that products meet regulatory standards, pharmacists in these roles are responsible for the quality of medications before they reach the market.
- Regulatory Affairs: Pharmacists in regulatory roles ensure that pharmaceutical products comply with laws and regulations, working closely with government agencies to secure approvals.
- Manufacturing: Involved in the production process, pharmacists oversee manufacturing and packaging of pharmaceutical products, ensuring that they are produced safely and effectively.
- Warehousing and Supply Chain Management: Pharmacists manage the storage, distribution, and logistics of pharmaceutical products, ensuring that medications are handled and delivered under proper conditions to maintain their efficacy and safety.
- Dispensing: Pharmacists ensure accurate dispensing of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and raw materials within manufacturing settings, ensuring that these substances are handled and distributed according to strict regulatory standards and industry protocols.
- Sales and Marketing: Pharmacists use their knowledge to promote pharmaceutical products, providing information to healthcare professionals and consumers.
- Business Development: Pharmacists involved in business development identify new opportunities for growth within the pharmaceutical industry, including expanding markets, partnerships, and product lines, leveraging their knowledge of the industry to drive business success.
2. Community Pharmacy
- Community Pharmacist: Multifaceted and vital role in the healthcare system. Community pharmacists work at the intersection of healthcare and the community, providing essential services that ensure optimal medication use and promote overall health.
- Dispensing Pharmacist: A dispensing pharmacist plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications. Their responsibilities focus on the accurate preparation and distribution of pharmaceuticals to patients, alongside offering crucial support and guidance.
- Retail Pharmacist: A retail pharmacist, also known as a community pharmacist, plays a vital role in the healthcare system by providing a range of services to the public within a retail pharmacy setting. Their responsibilities extend beyond dispensing medications to include patient care, education, and community health support.
3. Hospital Pharmacy
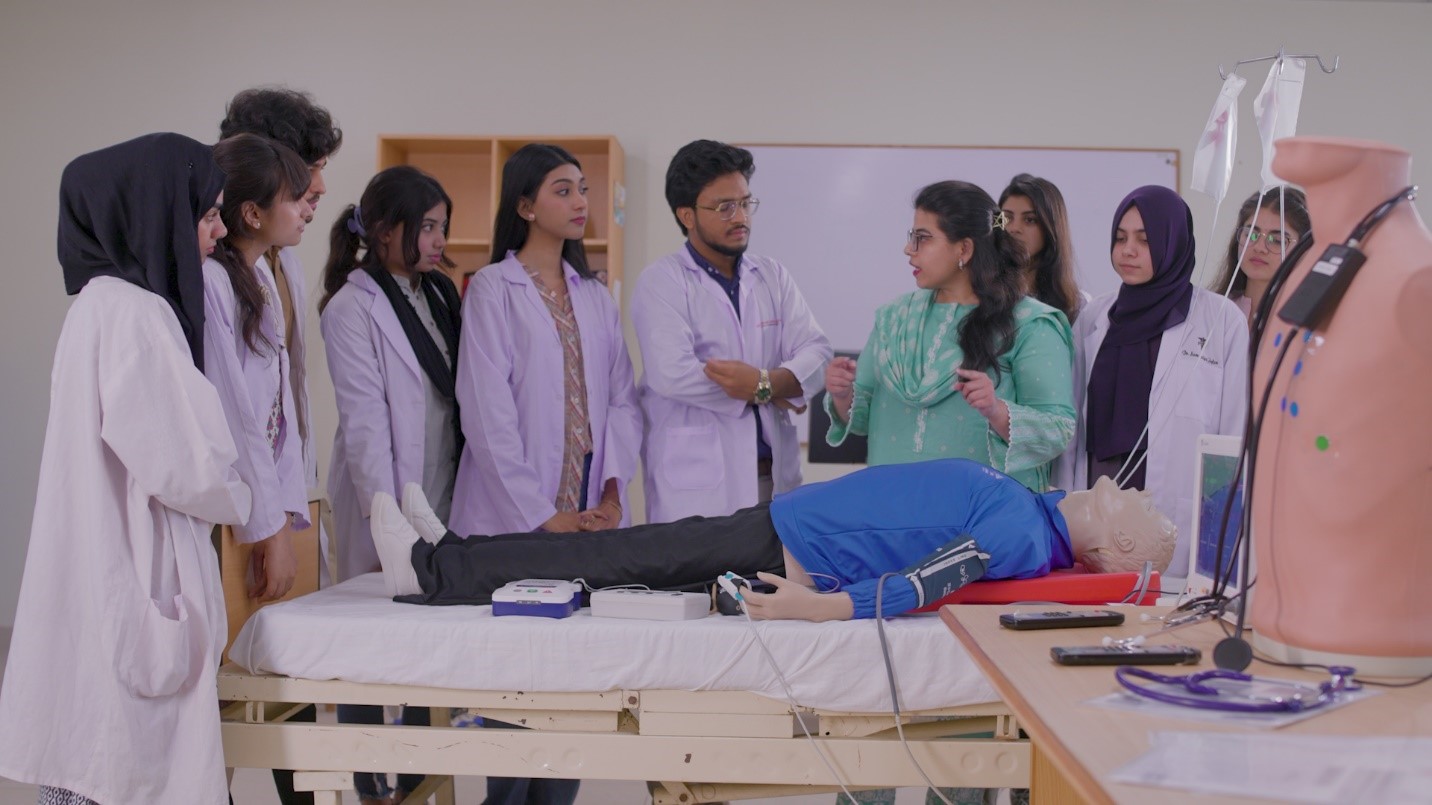

A hospital pharmacist plays a crucial role in the healthcare team within a hospital setting. Their responsibilities are focused on ensuring the safe, effective, and efficient use of medications for hospitalized patients.
- Prescription Review: Review and verify medication orders from healthcare providers for accuracy, appropriateness, and potential interactions.
- Medication Preparation: Prepare and dispense medications, including intravenous (IV) solutions and compounds, ensuring the correct dosage and administration methods.
- Therapeutic Monitoring: Monitor patient responses to medications, including efficacy and adverse effects, and adjust therapy as needed.
4. Academics
Academia offers pharmacists a fulfilling career path focused on education, research, and shaping the future of the profession. Here are some key aspects of pursuing a career in academia as a pharmacist:
- Teaching and Education: Pharmacists in academia educate the next generation of pharmacy professionals. They develop and deliver lectures, design curricula, and mentor students in various aspects of pharmaceutical science and practice.
- Research and Innovation: Academic pharmacists engage in cutting-edge research, contributing to advancements in drug development, healthcare practices, and pharmaceutical science. They often publish their findings in scientific journals, influencing the broader scientific community.
- Preceptorship: Many academic pharmacists serve as preceptors for clinical training, guiding and teaching undergraduate students in clinical settings. This dual role allows them to mentor and educate future pharmacists, ensuring students gain hands-on experience and practical skills essential for their professional development.
- Curriculum Development: Pharmacists in academia play a critical role in designing and updating educational programs, ensuring that the curriculum remains relevant and prepares students for the evolving landscape of pharmacy practice.
- Leadership and Administration: Academic pharmacists may take on leadership roles within their institutions, such as department chairs or deans, overseeing the development of academic programs and managing faculty and resources.
- Professional Development: Academia provides opportunities for continuous learning and professional growth. Pharmacists can pursue advanced degrees such as M.Phil., Ph.D., or M.S., attend conferences, and participate in professional organizations to stay at the forefront of their field.
- Community Engagement: Academic pharmacists often engage with the community through outreach programs, health education initiatives, and partnerships with healthcare organizations, contributing to public health and awareness.
5. Regulatory/Government Jobs
- DRAP (Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan): Regulates drug safety, quality, registration, and marketing of pharmaceuticals in Pakistan.
- DTL (Drug Testing Laboratory): Tests and certifies drug quality and safety.
- Drug Inspector: Ensures compliance with drug laws through inspections.
- Procurement Officer: Acquires quality pharmaceuticals for government healthcare.
- Anti-Narcotic Office: Combats illegal narcotics production and distribution.
- Various Other Government Health Sectors: Focus on public health, policy, and administration.
6. Entrepreneurship
- Pharmacy/Medical Store: Dispenses medications and provides healthcare products to the community.
- Medicine Distribution: Oversees the supply chain and delivery of pharmaceuticals to pharmacies and healthcare facilities.
- Warehouse: Stores and manages pharmaceutical inventory, ensuring proper handling and distribution.
- Retail: Provides pharmaceutical services and patient counseling in community pharmacies abroad.
Internship Opportunities as
- Hospital and Clinical Pharmacist
- Industrial Pharmacist
Eligibility Criteria
- Have 60% marks in HSC (Pre-Medical) or 60% marks in A-level or equivalent qualification
- Qualify the Aptitude Test and Interview
Scheme of Study (Semester Wise)
- Duration: 5 Years
- Semesters: 10
- Credit Hours: 206
1st Year
Semester - Ⅰ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| ENG 111 | English – A (Functional English) | 2 |
| PHM 101 | Anatomy and Histology | 3 |
| PHM 101(Lab) | Anatomy and Histology | 1 |
| PHM 103 | Physiology – A | 3 |
| PHM 103 Lab) | Physiology – A | 1 |
| PHM 105 | Pharmaceutics – IA (Physical Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 105 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics – IA (Physical Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 107 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IA (Organic) | 2 |
| PHM 107 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IA (Organic) | 1 |
| PHM 109 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIA (Biochemistry) | 3 |
| PHM 109 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIA (Biochemistry) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 21 |
Semester - Ⅱ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| ENG 112 | English – B (Communication & Writing skills) | 4 |
| PHM 102 | Physiology – B | 3 |
| PHM 102 (Lab) | Physiology – B | 1 |
| PHM 104 | Pharmaceutics – IB (Physical Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 104 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics – IB (Physical Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 106 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IB (Organic) | 2 |
| PHM 106 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IB (Organic) | 1 |
| PHM 108 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIB (Biochemistry) | 3 |
| PHM 108 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIB (Biochemistry) | 1 |
| PHM 110 | Pharmacy Practice – IA (Pharmaceutical Mathematics) | 3 |
| Total Credit Hours | 22 |
2nd Year
Semester - Ⅲ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| IST 101 | Islamic Studies | 2 |
| PHM201 | Pharmaceutics-IIA (Dosage Forms, Science and Calculations) | 3 |
| PHM 201 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-IIA (Dosage Forms, Science and Calculations) | 1 |
| PHM 203 | Pathology | 3 |
| PHM 203 (Lab) | Pathology | 1 |
| PHM 205 | Pharmaceutics-IIIA (Pharmaceutical Microbiology) | 3 |
| PHM 205 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-IIIA (Pharmaceutical Microbiology) | 1 |
| PHM 207 | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IA | 3 |
| PHM 207 (Lab) | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IA | 1 |
| PHM 209 | Pharmacognosy – IA Basic | 3 |
| PHM 209 (Lab) | Pharmacognosy – IA Basic | 1 |
| PHM 211 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice –(Introductory Pharmacy Practice experience) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 23 |
Semester - Ⅳ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PST101 | Pakistan Studies | 2 |
| PHM 202 | Pharmaceutics – IIB (Dosage Forms science & calculations) | 3 |
| PHM 202 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics – IIB (Dosage Forms science & calculations) | 1 |
| PHM 204 | Pharmaceutics – IIIB (Pharmaceutical Immunology) | 3 |
| PHM 204 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics – IIIB (Pharmaceutical Immunology) | 1 |
| PHM 206 | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IB | 3 |
| PHM 206 (Lab) | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IB | 1 |
| PHM 208 | Pharmacognosy – IB (Basic) | 3 |
| PHM 208 (Lab) | Pharmacognosy – IB (Basic) | 1 |
| PHM 210 | Pharmacy Practice – IB (Bio-statistics) | 3 |
| PHM 212 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – (Introductory Pharmacy Practice Experience) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 22 |
3rd Year
Semester - Ⅴ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 301 | Pharmacy Practice – IIA (Dispensing Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 301 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – IIA (Dispensing Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 303 | Pharmacy Practice – IVA ( Hospital Pharmacy) | 2 |
| PHM 303 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – IVA ( Hospital Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 305 | Pharmacy Practice – VA (Clinical Pharmacy-I) | 3 |
| PHM 405 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – VA (Clinical Pharmacy-I) | 1 |
| PHM 307 | Pharmacology and Therapeutics-IIA | 3 |
| PHM 307 (Lab) | Pharmacology and Therapeutics-IIA | 1 |
| PHM 309 | Pharmacognosy – IIA (Advanced) | 3 |
| PHM 309 (Lab) | Pharmacognosy – IIA (Advanced) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 19 |
Semester – Ⅵ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 302 | Pharmacy Practice – IIB (Community Pharmacy, Social and administrative Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM304 | Pharmacy Practice – IVB (Hospital Pharmacy) | 2 |
| PHM 304 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – IVB (Hospital Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 306 | Pharmacy Practice – VB (Clinical Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 306 (Lab.) | Pharmacy Practice – VB (Clinical Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 308 | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IIB | 3 |
| PHM 308 (Lab) | Pharmacology and Therapeutics – IIB | 1 |
| PHM 310 | Pharmacognosy – IIB (Advanced Pharmacognosy and CAM) | 3 |
| PHM 310 (Lab) | Pharmacognosy – IIB (Advanced Pharmacognosy and CAM) | 1 |
| PHM 312 | Pharmacy Practice – III (Computer and its Applications in Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 312 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice – III (Computer and its Applications in Pharmacy) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 22 |
4th Year
Semester - Ⅶ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 401 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIIA) (Pharmaceutical Analysis) | 3 |
| PHM 401 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIIA) (Pharmaceutical Analysis) | 1 |
| PHM 403 | Pharmacy Practice-VIA (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy II) | 3 |
| PHM 403 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice-VIA (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy II) | 1 |
| PHM 405 | Pharmaceutics-IVA (Industrial Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 405 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-IVA (Industrial Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 407 | Pharmaceutics-VA (Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics) | 3 |
| PHM 407 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-VA (Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics) | 1 |
| PHM 409 | Pharmaceutics-VIA (Pharmaceutical Quality Management) | 3 |
| PHM 409 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-VIA (Pharmaceutical Quality Management) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 20 |
Semester – Ⅷ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 402 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIIB (Pharmaceutical Analysis) | 3 |
| PHM 402 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry – IIIB (Pharmaceutical Analysis) | 1 |
| P1HM 404 | Pharmacy Practice – VIB (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy-II) | 3 |
| PH3M 404 (Lab) | Pharmacy Practice-VIB (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy-II) | 1 |
| PHM 406 | Pharmaceutics-IVB (Industrial Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 406 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-IVB (Industrial Pharmacy) | 1 |
| PHM 408 | Pharmaceutics-VB (Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics) | 3 |
| PHM 408 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-VB (Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics) | 1 |
| PHM 410 | Pharmaceutics-VIB (Pharmaceutical Quality Management) | 3 |
| PHM 410 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-VIB (Pharmaceutical Quality Management) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 20 |
5th Year
Semester - Ⅸ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 501 | Pharmaceutics-VIIA (Pharmaceutical Technology) | 3 |
| PHM 501 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics-VIIA (Pharmaceutical Technology) | 1 |
| PHM 503 | Pharmacy Practice-VIIA (Forensic Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 505 | Pharmacy Practice-VIIIA (Pharmaceutical Management & Marketing) | 3 |
| PHM 507 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IVA (Medicinal Chemistry) | 3 |
| PHM 507 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IVA (Medicinal Chemistry) | 1 |
| PHM 509 | Pharmacy Practice – XII A (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy III) | 2 |
| PHM 511 | Pharmacy Practice – XI A (Advanced Pharmacy Practice Experience) | 2 |
| PHM 513 | Pharmacy Practice – IX (Research Methodology) | 1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 19 |
Semester - Ⅹ
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PHM 502 | Pharmaceutics – VIIB (Pharmaceutical Technology) | 3 |
| PHM 502 (Lab) | Pharmaceutics – VIIB (Pharmaceutical Technology) | 1 |
| PHM 504 | Pharmacy Practice – VIIB (Forensic Pharmacy) | 3 |
| PHM 506 | Pharmacy Practice – VIIIB (Pharmaceutical Management and Entrepreneurship) | 3 |
| PHM 508 | Pharmaceutical Chemistry- IVB (Medicinal Chemistry) | 3 |
| PHM 508 (Lab) | Pharmaceutical Chemistry- IVB (Medicinal Chemistry) | 1 |
| PHM 510 | Pharmacy Practice – XII B (Advanced Clinical Pharmacy III) | 2 |
| PHM 512 | Pharmacy Practice – XI B (Advance Pharmacy Practice Experience) | 2 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 |