Dean's Message
The Faculty of Engineering aims to develop and produce the next generation of accomplished engineers, scientists, researchers, innovators, and entrepreneurs with strong technical and analytical skills. We offer two four-year undergraduate degree programs: B.E. in Biomedical Engineering and BS in Robotics and Intelligent Systems, along with ME and PhD programs in Biomedical Engineering. Our engineering program is recognized and accredited by the Pakistan Engineering Council (PEC).
The B.E. Biomedical Engineering program is designed to produce engineers with a competitive edge in both knowledge and technical skills through inquiry, research, and experimentation. On the other hand, the B.S. in Robotics and Intelligent Systems program focuses on robotics and intelligent system analysis and application, preparing students to meet the growing global demand in these cutting-edge fields.
For both programs, the faculty of engineering has adopted a globally competitive curriculum that incorporates theoretical knowledge with hands-on training and learning using state-of-the-art equipment. This allows students to solve complex engineering problems and enables them to enhance their technical skills in various industries such as automation, artificial intelligence, and healthcare, both nationally and internationally.
Our well-qualified and experienced faculty ensures that the program's learning outcomes are achieved. We emphasize student-teacher interaction to provide an optimal learning environment, where strong emphasis is laid on Industry-Academia collaboration. To support this, we have an Industrial Advisory Board that facilitates the development of insights on current trends in the healthcare industry and emerging technologies by arranging class lectures, seminars, webinars, field visits, and workshops for students.
For continuous quality improvement, the Board of Studies and Board of Faculty regularly review and discuss curricula and related matters, ensuring that our programs remain relevant and up-to-date. On behalf of the Faculty of Engineering, I welcome you to join an innovative world of Engineering and Science and wish you all the best in your future endeavours.
Dr. M. Zeeshan Ul Haque
Professor & Dean
Faculty of Engineering
Department of Biomedical Engineering
The Faculty of Engineering offers a variety of programs in engineering, science, and technology. These programs aim to improve educational standards and solve real-world problems through ideas and innovation. Our programs focus on engineering and computing principles, problem-solving approaches, and the development of innovative solutions in healthcare, robotics, and intelligent systems
As technology advances, the global demand for biomedical, robotics, and AI experts is rising globally. To meet this demand, we offer two four-year, well-structured undergraduate degree programs: BE Biomedical Engineering and BS Robotics and Intelligent Systems, along with ME and PhD in Biomedical Engineering. All programs follow the Higher Education Commission (HEC) and the Pakistan Engineering Council (PEC) guidelines, ensuring compliance with the Outcome-Based Education (OBE) system.
Our curriculum is designed to provide a solid engineering foundation coupled with hands-on expertise in state-of-the-art laboratories. The BE Biomedical Engineering program focuses on integrating engineering with medical sciences, covering areas such as medical device design, bioinstrumentation, and healthcare technology management. The BS Robotics and Intelligent Systems program covers robotics, AI, Machine Learning, and Autonomous Systems, preparing students for technological advancement.
The ME Biomedical Engineering programs emphasize advanced areas such as Physiological Modeling and simulation, Biomedical Imaging, Signal Processing, Medical device design and the application of AI and health care. The PhD Biomedical Engineering program is designed to unlock new frontiers in Biomedical research, equipping graduates with the expertise to lead cutting-edge research and innovation in health care.
Beyond regular classes, we enhance technical and professional skills through seminars, workshops, and internships, preparing students for research, development, and innovation. Our experienced faculty, modern infrastructure, and supportive environment help turn theoretical knowledge into real world solutions for future engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs.
To maintain continuous improvement and high educational standards, the Faculty of Engineering has established a Board of Studies (BoS), a Board of Faculty (BoF), and an Industrial Advisory Board (IAB) made up of professionals, industry experts, entrepreneurs, and consultants. These bodies guide student’s professional development, ensuring their ability to secure job placement and entrepreneurial opportunities.
Advisory Experts from Industry
| S.no | Name | Designation | Organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Engr. Dennis John Mathews | Head of Biomedical and Electronics Engineering | Aga Khan University Hospital |
| 2 | Engr. Osama A.Qayoom | Head of Department of Biomedical Engineering | DOW University of Health Science (DUHS) |
| 3 | Engr. Farhan Pervez | Deputy General Manager | Medequips |
| 4 | Engr. Haris Baig | Founder and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) | Deneb Corporation (Pvt). Ltd. |
| 5 | Engr. M. Junaid Khan | Head of Department of Biomedical Engineering | National Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases (NICVD) |
| 6 | Engr. Mujeeb Khalil | Head of Department of Biomedical Engineering | Tabba Heart Institute |
| 7 | Engr. Wajahat Ali | Manager Biomedical Engineering | Darul Sehat Hospital |
| 8 | Engr. Syed Shuja Ur Rehman | Manager Sales | Noor International |
| 9 | Engr. Wajih Abidi | Manager Biomedical Engineering | Jinnah Post Graduate Medical Center (JPMC) |
| 10 | Engr. Azfar Hussain | Head of Customer Service Pakistan and Afghanistan | Siemens Healthineer |
| 11 | Engr. Faraz Alam Hashmi | HoD Biomedical Engineering | Abbassi Shaheed Hospital |
| 12 | Engr. Yasir Burney | Manager, Clinical Engineering | Aga Khan University Hospital |
| 13 | Saleem Pirani | Manager, Technology Support | Centre for Innovation in Medical Education, AKUH |
| 14 | Engr. Hammad Hussain | Deputy Manager Biomedical Department | SMBB Institute of Trauma (SMBBIT) |
| 15 | Engr. Muhammad Musaddiq | National Service Manager | Noor International |
Vision
To be recognized as an excellent academic, research-driven, innovative, and entrepreneurial education provider in the field of engineering and sciences through advanced knowledge and educational methods for the solution to problems in Healthcare, Robotics, and Intelligent Systems..
Mission
To provide an optimum learning environment to educate future engineers in the fields of Biomedical Engineering, Robotics, and Intelligent Systems utilizing the most updated curricula and training opportunities that enhance the interpersonal, entrepreneurial and multidisciplinary knowledge to contribute in academia, research centres and industry.
Objectives
The objectives of the department of biomedical engineering is to deliver quality education by:
- Providing student-centered degree programs ensuring graduates are accomplished in academic, technical and entrepreneurial expertise.
- Providing graduates with opportunities that fosters professional development, ethical responsibilities and lifelong learning.

BE Biomedical Engineering
The Bachelor of Engineering (BE) in Biomedical Engineering at Salim Habib University is a comprehensive four-year degree program designed to provide students with the essential skills and knowledge needed to excel in the rapidly evolving fields of biomedical technology, healthcare innovation, and medical device development.
The program is meticulously crafted to meet the demands of both academic and industrial careers, ensuring that students graduate with a strong foundation in the principles of biomedical engineering and are well-prepared to:
- Innovate in the development and improvement of medical devices and technologies.
- Apply engineering principles to solve complex healthcare challenges.
- Integrate biological sciences with engineering techniques to improve patient care.
- Engage in cutting-edge research and development within the biomedical industry.
- Collaborate effectively with professionals across multidisciplinary teams in healthcare and engineering settings.
This program not only prepares students for immediate entry into the workforce but also provides a solid foundation for further studies and research in biomedical engineering and related fields.
Interdisciplinary Expertise: Integration of knowledge from engineering, biology, and medicine to develop innovative solutions for real-world medical challenges.

Industry-Integrated Learning: Experiential learning through hands-on projects in collaboration with medical professionals, researchers, and industry experts, with opportunities for mentorship and networking.

High-Tech Careers: Develop marketable and entrepreneurial skills for exciting career opportunities and innovative solutions in a rapidly growing field, improving human health and quality of life.

Eligibility requirements
- 60% marks in HSSC (Pre-Engineering or Pre-Medical)/ A-levels, relevant B. Sc., DAE, B. Tech (Hons.) / B. Sc. Engineering Technology or equivalent qualification
- Qualify the Aptitude Test and Interview
- Eligibility Criteria as per PEC Policy
Program Mission
The mission of the Program is to provide students with an optimal learning environment and multidisciplinary education. The Program utilizes curricula, training and research opportunities to contribute in academia, research centers, healthcare industry and society with their profound analytical and design capabilities.
History of Interaction between DBME and Pakistan Engineering Council (PEC)
Bachelor of Engineering (B.E.) in Biomedical Engineering was launched after a successful PEC Zero Visit (ref: PEC/AD/SHU-K-BIO-MEDICAL/Zero/2017), dated August 4, 2017, granting permission to launch the program. In 2017, student induction began, followed by a successful interim visit (ref: PEC/EAD/SHU-K/BIOMED/RL-2019), dated July 16, 2019. Eventually, the Biomedical Engineering program at SHU was accredited after a successful accreditation visit (ref: PEC/EAD/SHU-K/DL-105/2022), dated February 1, 2022, by the Pakistan Engineering Council.
Transformation into Outcome Based Education (OBE) System
Department of Biomedical Engineering has implemented outcome based education (OBE) system as per PEC requirement with well-defined Program Education Objectives (PEOs) and Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs).
Program Education Objectives (PEOs):
PEOs are designed in accordance with the vision and mission of the department exhibiting the accomplishments that the graduates are expected to accomplish. It serves an important function in designing the curriculum, PLOs and subsequently
- The program enables Biomedical engineering graduates with the ability to apply integrated knowledge of mathematics, biosciences, information technology, engineering and management to identify and solve complex engineering problems and generate novel concepts for the professional and technological development in the health care industry.
- To enable BME graduates to effectively work in multidisciplinary team environments; communicating with a variety of audience, making decisions that are socially and ethically responsible for exhibiting their interpersonal, management and leadership skills.
- Biomedical engineering graduates who will build and expand upon their undergraduate foundations of knowledge and ethical values by engaging in life-long and continuous learning opportunities for advance career and professional training.
Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs):
In B. E. BME program, twelve (12) PLOs have been adopted from the graduate attributes for engineers defined in the PEC OBA manual, 2019. The following are the twelve PLOs adapted for the program:
- Engineering Knowledge An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, engineering fundamentals and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering problems.
- Problem Analysis An ability to identify, formulate, and analyze complex engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences.
- Design/Development of Solutions An ability to solve complex engineering problems and design systems, components or processes that meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations.
- Investigation An ability to investigate complex engineering problems in a methodical way including literature survey, design and conduct of experiments, analyzing and interpreting experimental data, and synthesizing information to derive valid conclusions.
- Modern Tool Usage An ability to create, select and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools, including prediction and modelling, to complex engineering activities, with an understanding of the limitations.
- The Engineer and Society An ability to apply reasoning informed by contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the responsibilities relevant to professional engineering practices and solutions to complex engineering problems.
- Environment and Sustainability An ability to understand the impact of professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts and demonstrate knowledge of and need for sustainable development.
- Ethics Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of engineering practices.
- Individual and Team Work An ability to work effectively, as an individual or as a team, on multifaceted and /or multidisciplinary settings.
- Communication An ability to communicate effectively, orally as well as in writing, on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give and receive clear instructions.
- Project Management An ability to demonstrate management skills and apply engineering principles to one’s own work, as a member and/or team leader, to manage projects in a multidisciplinary environment.
- Lifelong Learning An ability to recognize importance of, and pursue lifelong learning in the broader context of innovation and technological developments.
Consistency of Vision and Mission of DBME with Vision and Mission of SHU
| SHU Vision | DBME Vision |
| ✔ | ✔ |
| SHU Mission | DBME Mission |
| ✔ | ✔ |
Mapping of PEOs with DBME Vision and Mission Statements
| PEO 1 | PEO 2 | PEO 3 | |
| DBME Vision | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| DBME Mission | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Mapping of PLOs and PEOs
The twelve PLOs, defined for the Biomedical Engineering Program, are mapped to the three PEOs. Mapping of the PLOs to PEOs.
| PEO 1 | PEO 2 | PEO 3 | |
| Engineering Knowledge | ✔ | ||
| Problem Analysis | ✔ | ||
| Design/Development of Solutions | ✔ | ||
| Investigation | ✔ | ||
| Modern Tool Usage | ✔ | ||
| The Engineer and Society | ✔ | ||
| Environment and Sustainability | ✔ | ||
| Ethics | ✔ | ||
| Individual and Team Work | ✔ | ||
| Communication | ✔ | ||
| Project Management | ✔ | ||
| Lifelong Learning | ✔ |
Undergraduate Biomedical Engineering Curriculum Design
The curriculum is designed to provide knowledge, analytical and leadership abilities, critical thinking and ethical values to cope with technological challenges. Complex Engineering Problems (CEPs), Problem Based Learning (PBL) and Open Ended Labs (OELs) are also included in relevant courses to equip the students for lifelong learning as guided by OBE. The management courses provide students an insight of entrepreneurship and management skills.
Scheme Of Studies
Duration: 4 YearsSemesters: 8
Credit Hours:138(For Batches till 2023)
139(For Batch 2024 and onwards)
For 2024 batch and onwards
1st Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅰ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| PHC101 | Applied Physics | 2 + 1 | |
| BME101 | Introduction to Biomedical Engineering | 1 + 0 | |
| BME102 | Introduction to Computing | 2 + 1 | |
| ELE101 | Basic Electrical Engineering | 3 + 1 | |
| MTH 101/ BIO-101* | Basic Mathematics / Biology | 3 + 0 | |
| IST101 | Islamic Studies | 2 + 0 | |
| BSC100** | Introduction to Chemistry (only for ICS students) | 0 + 0 (NC) | |
| ENG107 | Functional English | 2 + 0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
Semester - Ⅱ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| PST101 | Pakistan Studies | 2 + 0 | |
| ENG103 | Communication Skills | 2 + 0 | |
| MTH103 | Calculus & Analytical Geometry | 3 + 0 | |
| BSC102 | Biochemistry | 2 + 1 | |
| CSC108 | Object Oriented Programming | 2 + 1 | |
| ELE102 | Basic Electronics | 3 + 1 | |
| BME-103 | Occupational Health and Safety | 1 + 0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
2nd Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅲ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MTH201 | Linear Algebra & Differential Equation | 3 + 0 | |
| PHY201 | Physiology I | 2 + 1 | |
| ELE201 | Circuit Analysis | 3 + 1 | |
| BME201 | Computer Aided Engineering Drawing | 0 + 1 | |
| ANA201 | Human Anatomy | 2 + 1 | |
| BME202 | Biomedical Electronics | 3 + 1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
Semester - Ⅳ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MTH202 | Complex Variable & Transformation | 3 + 0 | |
| ELE203 | Digital Logic Design | 3 + 1 | |
| BME203 | Biomechanics | 3 + 1 | |
| PHY202 | Physiology II | 2 + 1 | |
| BME204 | Biomedical Instrumentation I | 3 + 1 | |
| BME200*** | BME200***BIO-101* | Community Service | 0 + 0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
3rd Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅴ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| BME301 | Biomedical Instrumentation II | 3 + 1 | |
| ELE302 | Signals & Systems | 3 + 1 | |
| MTH301 | Statistics | 3 + 0 | |
| MTH302 | Numerical Analysis | 3 + 0 | |
| ELE301 | Microprocessor & Interfacing | 2 + 1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 17 | ||
Internship I (Mandatory) |
|||
Semester - Ⅵ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| BME303 | Bio-signal Processing | 3 + 1 | |
| BME304 | Modeling & Simulation | 2 + 1 | |
| BME305 | Biomedical Control Systems | 3 + 1 | |
| XXXxxx**** | Elective I | 3 + 0 | |
| BME306 | Biomaterials | 3 + 1 | |
| BME300*** | Internship Seminar | 0 + 0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
4th Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅶ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MGT401 | Entrepreneurship | 3 + 0 | |
| MGT402 | Engineering Management | 3 + 0 | |
| ENG401 | Technical Report Writing & Presentation Skills | 3 + 0 | |
| XXXxxx**** | Elective II | 3 + 0 | |
| XXXxxx**** | Elective III | 2 + 1 | |
| BME448 | Final Year Design Project –I | 0 + 3 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
Internship II (Highly Recommended) |
|||
Semester - Ⅷ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| BME498 | Final Year Design Project –II | 0 + 3 | |
| BME401 | Medical Imaging | 2 + 1 | |
| BME402 | Professional Practices & Ethics | 3 + 0 | |
| XXXxxx**** | Elective IV | 3 + 0 | |
| XXXxxx**** | Elective V | 3 + 0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 15 | ||
- * Basic Mathematics for pre-medical students and Biology for pre-engineering students.
- **Non-credit for intermediate computer science students (from batch spring 2024 – onwards)
- ***Non-credit from batches spring 2022- onwards
- ****Elective courses to be offered are subject to the availability of resources.
NB: This curriculum plan conforms to the NCRC 2017 guidelines of the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (HEC). Please refer to SHU website for latest information.
List of Electives
| Course Code | Course Title | Pre-requisites | Credit Hours |
| CSC 408 | Artificial Intelligence | N. A | 3 + 0 |
| BME 307 | Introduction to Molecular Biology | BSC 101, BSC 103 | 2 + 1 |
| BME 403 | Introduction to Bioinformatics | BME 307 | 2 + 1 |
| BME 321 | Telemedicine Systems | N. A | 3 + 0 |
| BME 411 | Rehabilitation Engineering | N. A | 2 + 1 |
| BME 421 | Medical Device Quality System and Standards | N. A | 3 + 0 |
| BME 422 | Hospital Information Management Systems | N. A | 3 + 0 |
For batches till 2023
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
1st Year |
||
Semester - Ⅰ |
||
| PHC101 | Applied Physics | 2+1 |
| BME102 | Introduction to Computing | 2+1 |
| ELE101 | Basic Electrical Engineering | 3+1 |
| MTH 101/ BIO-101* | Basic Mathematics / Biology | 3+0 |
| BME101 | Introduction to Biomedical Engineering | 1+0 |
| IST101 | Islamic Studies | 2+0 |
| ENG101 | Functional English | 0+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 16 | |
Semester - ⅠⅠ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| PST101 | Pakistan Studies | 2+0 |
| ENG103 | Communication Skills | 2+0 |
| MTH103 | Calculus & Analytical Geometry | 3+0 |
| BSC102 | Biochemistry | 2+1 |
| CSC103 | Object Oriented Programming | 3+1 |
| ELE102 | Basic Electronics | 3+1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | |
2nd Year |
||
Semester - ⅠⅠⅠ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| MTH201 | Linear Algebra & Differential Equation | 3+0 |
| PHY201 | Physiology I | 2+1 |
| ELE201 | Circuit Analysis | 3+1 |
| BME201 | Computer Aided Engineering Drawing | 0+1 |
| ANA201 | Human Anatomy | 2+1 |
| BME202 | Biomedical Electronics | 3+1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | |
Semester - ⅠⅤ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| MTH202 | Complex Variable & Transformation | 3+0 |
| ELE203 | Digital Logic Design | 3+1 |
| BME203 | Biomechanics | 3+1 |
| PHY202 | Physiology II | 2+1 |
| BME204 | Biomedical Instrumentation I | 3+1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | |
3rd Year |
||
Semester - Ⅴ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| BME301 | Biomedical Instrumentation II | 3+1 |
| ELE302 | Signals & Systems | 3+1 |
| MTH301 | Statistics | 3+0 |
| MTH302 | Numerical Analysis | 3+0 |
| ELE301 | Microprocessor & Interfacing | 2+1 |
| Total Credit Hours | 17 | |
Semester - ⅤⅠ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| BME303 | Bio-signal Processing | 3+1 |
| BME304 | Modeling & Simulation | 2+1 |
| BME305 | Biomedical Control Systems | 3+1 |
| XXXxxx*** | Elective I | 3+0 |
| BME306 | Biomaterials | 3+1 |
| BME300** | Internship Seminar | 0+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | |
4th Year |
||
Semester - ⅤⅠⅠ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| MGT401 | Entrepreneurship | 3+0 |
| MGT402 | Engineering Management | 3+0 |
| ENG401 | Technical Report Writing & Presentation Skills | 3+0 |
| XXXxxx *** | Elective II | 3+0 |
| XXXxxx *** | Elective III | 2+1 |
| BME449**** | Final Year Design Project –I | 0+3 |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | |
Semester - ⅤⅠⅠⅠ |
||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| BME449**** | Final Year Design Project –II | 0+3 |
| BME401 | Medical Imaging | 2+1 |
| BME402 | Professional Practices & Ethics | 3+0 |
| XXXxxx*** | Elective IV | 3+0 |
| XXXxxx *** | Elective V | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 15 | |
| Track 1 | Track 2 | Track 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Instrumentation | Tissue Engineering and Molecular Bioengineering | Biomedical Computing |
| Biomedical Engineering Systems | Biophysics | Telemedicine Systems |
| Medical Device Quality System and Standards | Biofluid Mechanics & Bioheat Transfer | Medical Data System |
| Medical Device Regulatory Affairs | Tissue Engineering | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| Power Electronics | Genetic Engineering | Artificial Intelligence |
| Medical Robotics | Nano Biotechnology | Bioinformatics |
| Rehabilitation Engineering | DNA Computing | Medical Image Processing |
| Bioelectricity | Regenerative Medicine | Hospital Information System |
| Drug Delivery Systems | ||
| Neuroscience |
- * Basic Mathematics for pre-medical students and Biology for pre-engineering students.
- **Non-credit
- ***Elective courses are selected from the suggestions of IAB, followed by the approval of statutory bodies.
- ****Final year project marks calculated in 8th semester
Internship Opportunities
- Healthcare centers
- Research laboratories
- Medical device industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
Career Prospects
Graduates will find opportunities in:
- Biomedical departments in hospitals
- Academics and higher education
- Medical device manufacturers’ representatives
- Government regulatory institutions
- R&D organizations involved in analyzing, modeling and designing medical devices, systems, components or processes
Activities
Seminars/Webinars/Workshops
DBME plan, organize and put into effect various seminar/webinar/events in order to enlighten and enhance students learning in the field through interaction with professionals.
Industrial Visits/trainings/collaborations
DBME arranges various industrial visits for students to bridge the gap between academia and industry providing an opportunity for active/interactive learning experiences in class and outside the classroom environment. This enhances interpersonal and communication skills of the students.
ME Biomedical Engineering
The Master of Engineering (ME) in Biomedical Engineering is an interdisciplinary postgraduate program designed to advance students' expertise in the application of engineering principles to improve human healthcare through innovative technology. This program provides rigorous training, requiring students to build a strong foundation in biology, physiology, and mathematics, alongside advanced biomedical engineering coursework.
Interdisciplinary Expertise: Integration of knowledge from medical device design, standards and validation of medical devices and implants and AI in healthcare to develop solutions for real-world medical challenges.

Industry-Integrated Learning: Experiential learning in collaboration with national and international medical professionals, researchers, and industry experts, with opportunities for mentorship and networking.

High-Tech Careers: Develop marketable and entrepreneurial skills for exciting career opportunities and innovative solutions in a rapidly growing field, improving human health and quality of life.

Eligibility Requirements
- Sixteen years of education or 4-years Bachelor’s degree (BS/BE/BSc) after HSSC, A-levels or equivalent board
- Minimum 128 credit hours completed in BS/B.E./B.Sc. accredited by Pakistan Engineering Council In Biomedical, Mechanical, Electronics, Chemical, Telecommunication, Material, Electrical, Mechatronics, Computer, Software Engineering from HEC recognized Universities/Institutes with at least 2.5 CGPA or 60% marks
- The students have to clear the SHU entry test with a minimum 50% score in each section (Subject & English).
- OR
- If a candidate has already qualified the International (Subject) GRE/GAT/NTS, he/she will be exempted from the SHU entry test. The validity of International (Subject) GRE/GAT (International) is 5 years and that of NTS is two years.
Program Details
Why ME Biomedical Engineering?
Biomedical Engineering is an Interdisciplinary integrated field of engineering that aims to improve human healthcare through innovative use of technology. The Master of Engineering (ME) is a post graduate degree program designed to provide advanced training in biomedical engineering which requires students to establish the necessary foundation in biology, physiology and mathematics, in addition to advanced biomedical engineering coursework. Additionally, students are required to carry out research work and/or complete an approved project. During the postgraduate studies, students are expected to develop strong understanding of both biological processes and engineering, allowing them to bring improvements in hospitals, clinical setups, medical research centers and healthcare industry.
Program Vision
To produce research-driven, innovative and entrepreneurial expert personnel in the field of Biomedical Engineering by imparting quality interdisciplinary education through high quality academician and researchers for the benefit of society and healthcare community.
Program Mission
To provide students with a dynamic learning, and academic environment that encourages excellence in both teaching and research. As a result, assisting in becoming skilled, innovative, and socially responsible professional in the fields of academia, research, the healthcare sector, and the society.
Program Education Objectives (PEOs)
- Postgraduates with an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, biomedical sciences, IT, engineering and management to solve complex engineering problems and will continue developing the necessary skills to obtain leadership positions and other positions of increasing responsibilities.
- Postgraduates capable of effectively working in multidisciplinary team environments and communicate to a variety of audiences, making decisions that are socially and ethically responsible and exhibiting their interpersonal, management and leadership skills.
- Postgraduates capable of generating innovative concepts and novel research in biomedical engineering for the professional and technological development in the healthcare industry.
Program Structure
- Total Credit Hours (course-based): 30 Cr. Hr. coursework
- Total Credit Hours (Research-based): 24 Cr. Hr. coursework & 6 Cr. Hr. research work
-
Coursework (24 Credit Hours):
- Core Courses: Students are required to complete 12-credit hours of core courses for developing the advanced knowledge in the field of biomedical engineering.
- Elective Courses: Students are required to complete at least 12-credit hours of specialized advanced courses that are customized to student's research interests. If a student wants to complete the master degree by coursework, then they are required to complete an additional 6-credit hours of elective courses.
-
Research work (6 Credit Hours):
- Lab Rotations: Provide introductory experience to students in different research areas of the biomedical engineering field.
- Thesis Research: The student needs to complete an in-depth research project under the guidance of experienced and qualified faculty members.
- Seminars and Workshops: Students should participate regularly in departmental seminars, trainings, and workshops to stay updated with the latest research.
Admission Requirements
Educational Background
- Sixteen years of education or 4-year Bachelor’s degree (BS/BE/BSc) after HSSC, A-levels or equivalent board
- Minimum 128 credit hours completed in BS/B.E./B.Sc. accredited by the Pakistan Engineering Council In Biomedical, Mechanical, Electronics, Chemical, Telecommunication, Material, Electrical, Mechatronics, Computer, and Software Engineering from HEC recognized Universities with at least 2.5 CGPA or 60% marks
Admission Tests
- The students have to clear the SHU entry test with a minimum 50% score in each section (Subject & English). OR
- If a candidate has already qualified for the International (Subject) GRE/GAT/NTS, he/she will be exempted from the SHU entry test. The validity of International (Subject) GRE/GAT (International) is 5 years and that of NTS is two years.
- An interview must be cleared that shall aim to assess the research knowledge, experience, and aptitude of the applicant.
ME Biomedical Engineering Curriculum
The ME Biomedical Engineering program has been designed by the HEC’s stipulated semester credit hour requirement and is in complete compliance with the HEC/PEC NCRC 2017 curriculum guidelines. The semester-wise curriculum breakup for ME in Biomedical Engineering is given below:
ME Biomedical Engineering (Course-Based) |
||
Semester Ⅰ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-701 | Research Methodology | 3+0 |
| BME-703 | Modeling & Simulation of Physiological Systems | 3+0 |
| BME-704 | Advanced Biomedical Signals & Systems | 3+0 |
| BME-705 | Advanced Biomedical Instrumentation | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 12+0 | |
Semester Ⅱ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-7xx | Elective-I | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-II | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-III | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 9+0 | |
Semester Ⅲ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-7xx | Elective-IV | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-V | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-VI | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 9+0 | |
| Total ME credit hours | 30+0 | |
ME Biomedical Engineering (Research-Based) |
||
Semester Ⅰ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-701 | Research Methodology | 3+0 |
| BME-703 | Modeling & Simulation of Physiological Systems | 3+0 |
| BME-704 | Advanced Biomedical Signals & Systems | 3+0 |
| BME-705 | Advanced Biomedical Instrumentation | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 12+0 | |
Semester Ⅱ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-7xx | Elective-I | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-II | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-III | 3+0 |
| BME-7xx | Elective-IV | 3+0 |
| Total Credit Hours | 12+0 | |
Semester Ⅲ and onwards |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-799 | Master Thesis | 0+6 |
| Total Credit Hours | 0+6 | |
| Total ME credit hours | 24+6 | |
List of Elective Courses
- BME 712 Advanced Digital Signal Processing
- BME 722 Embedded Systems & Applications
- BME 723 Design of Medical Devices
- BME 724 Medical Microsystems
- BME 725 Biomedical Sensors
- BME 731 Advanced Rehabilitation Engineering
- BME 732 Invasive and non-Invasive Brain Computer Interfaces
- BME 733 Neural engineering
- BME 741 Medical Informatics
- BME 742 Biostatistics
- BME 751 Advanced Biomaterials
- BME 752 Biomaterials and Drug Delivery
- BME 753 Cell and Molecular Biology
- BME 761 Advanced Biomechanics
- BME 771 Operations Management
- BME 772 Pattern Recognition
- BME 773 Telemedicine System
- BME 774 Advanced Medical Image Processing
- BME 775 Advanced Medical Imaging
- BME 781 Ultrasonic Instrumentation and Imaging
- BME 782 Advances in Tissue Engineering
- BME 783 Advanced Bio-Fluid Mechanics
- A minimum of 9 credit hours of deficiency courses may be taken by the MPhil/MS/ME students, who wish to conduct their research in a related field but they lack specific knowledge/expertise in the new field. If required, additional deficiency courses should be offered decided by the Chairperson/Supervisor/Student.
- Any pre-requisite (deficiency) courses will be treated as credit course and must complete before offering credit-based courses.
- The department may offer core/elective courses from the given list (but not limited to) according to the availability of resources.
Placements and Careers Prospects
- Biomedical equipment management
- Biomedical consultant and entrepreneur
- Biomedical scientist and researcher
- Product development
- Equipment testing and validation
- Senior biomedical engineer
- Biomedical quality assurance manager
Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering
The PhD program in Biomedical Engineering at Salim Habib University is an advanced research degree program that combines knowledge of the medical sciences with engineering principles to address healthcare issues. The goal of the PhD program in biomedical engineering is to train aspirational scientists who are passionate about advancing medical science by fusing engineering principles with biological and medical sciences. Our curriculum offers a unique opportunity to learn more about the field of biomedical engineering. The curriculum will include expert-designed electives that are customized to each student's research interests in addition to courses in engineering physiology, biostatistics, and biomedical research ethics. In addition, students get the opportunity to work with faculty experts and gain real-world research experience in cutting-edge labs.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Engage in cutting-edge research, synthesising models and high-tech engineering principles to develop innovative solutions for real-world challenges, to transform the healthcare sector.
- Mentorship: Learn how to integrate emerging technologies to develop smart solutions under the guidance of professors with rich multidisciplinary experience.
- Hi-tech Laboratories: Gain hands-on experience in laboratories with high-tech equipment, enabling experimental analysis to produce novel research and solutions to solve complex problems.
- Research Opportunities: Explore a broad spectrum of research projects on rehabilitation engineering, biomaterials and tissue engineering, artificial intelligence and medical device design, advanced physiological modelling, standardisation and regulation of medical devices, and more.
- Collaborations: Benefit from opportunities for national and international collaborations and linkages to produce marketable solutions with global impact.
Degrees Offered
Degree: Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D) in Biomedical Engineering
Total Credit Hours (Research-based): 18 Cr. Hr. coursework & 30 Cr. Hr. research work
Program Structure
-
Coursework (18 Credit Hours):
- Core Courses: Courses related to engineering physiology, ethics, biostatistics, and effective communication in biomedical engineering for developing the generalized knowledge of students in the field of biomedical engineering.
- Elective Courses: Specialized and advanced courses like Physiological modeling, biomedical sensors and instrumentation, Biomedical systems and imaging, biomedical signal processing, tissue engineering, biomaterials that are customized to student's research interests.
-
Research work (30 Credit Hours):
- Lab Rotations: Provide introductory experience to students in different research areas of the biomedical engineering field.
- Thesis Research: The student needs to complete an in-depth research project under the guidance of experienced and qualified professors.
- Seminars and Workshops: Students should participate regularly in departmental seminars, trainings, and workshops to stay updated with the latest research.
Research Opportunities
The PhD candidates can choose from a variety of research areas to investigate, such as:
- Developing novel medical devices and imaging technologies
- Advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials
- Development of biological system computational models, etc.
Admission Requirements
Educational Background
HEC-recognised Master’s degree (MS, MPhil or equivalent) (with research) in a relevant discipline with a minimum CGPA of 3.0 out of 4.0 (in the semester system) or First Division (in the annual system).
Admission Tests
- The students have to clear the SHU entry test equivalent to the GRE/HAT general with a passing score of 60%. OR
- SHU accepts a test equivalent to GRE/HAT General, conducted by the testing bodies accredited by HEC, with a passing score of 60%.
- An interview must be cleared that shall aim to assess the research knowledge, experience, and aptitude of the applicant.
Ph.D Curriculum in Biomedical Engineering
Summary of Ph.D Program in Biomedical Engineering
| Duration | Minimum: 3 years and Maximum: 8 years |
| Number of semesters | 6-16 |
| Number of weeks per semester | 18 (16 weeks for teaching including midterm examinations and 2 weeks for examinations) |
| Number of core courses | 4 |
| Number of elective courses | 3 |
| Total number of credit hours for core courses | 9 |
| Total number of credit hours for elective courses | 9 |
| Total number of credit hours for coursework completion | 18 |
| Number of coursework credit hours per semester | 9 |
| Comprehensive examination | Compulsory (after successful completion of Ph.D coursework) |
| Number of credit hours for Ph.D research work | 30 |
Scheme of Studies for Ph.D in Biomedical Engineering
Semester - Ⅰ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-801 | Essentials of Biomedical Research, Ethics and Applications | 2 |
| BME-802 | Biostatistics for Engineers | 2 |
| BME-803 | Effective Communication and Presentation skills | 2 |
| BME-804 | Quantitative Physiology for Engineers | 3 |
| Total semester credit hours | 9 | |
Semester - ⅠⅠ |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-8xx | Elective I | 3 |
| BME-8xx | Elective II | 3 |
| BME-8xx | Elective III | 3 |
| Total semester credit hours | 9 | |
Semester - ⅠⅠⅠ & onwards |
||
| Course code | Course title | Credit hours |
| BME-899 | Ph.D Research work (Ph.D thesis) | 30 |
Elective Courses
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours |
| BME-811 | Advanced Modelling and Simulation of Physiological Systems | 3 |
| BME-812 | Advanced Biomedical Instrumentation and Design | 3 |
| BME-813 | Biomedical Sensors and Microsystems | 3 |
| BME-814 | Advanced Biomedical Signal Processing | 3 |
| BME-815 | Biomedical Engineering Design and Development | 3 |
| BME-821 | Biomedical Systems and Imaging | 3 |
| BME-822 | MRI and Biomedical Optics | 3 |
| BME-823 | Diagnostic Radiography and Imaging | 3 |
| BME-824 | Computer Methods in Biomedical Engineering | 3 |
Ph.D Degree Requirement
A Ph.D student should successfully complete the following components to obtain the degree in Ph.D in Biomedical Engineering from SHU.
Course Work
- Coursework of 18 credit hours is required to be completed and followed by successful completion of a comprehensive examination for granting candidacy as a Ph.D researcher. These 18 credit hours will be in addition to any pre-requisite courses offered by the department.
Comprehensive Examination
A Comprehensive Examination is required to be passed after completing Ph.D level courses.
Foreign Expert Evaluation
The Ph.D Dissertation must be evaluated by at least two Ph.D experts from technologically/academically advanced foreign countries in addition to local Committee members.
Open Defense
An open defense of Dissertation is an essential part of the Ph.D Program after a positive evaluation of the Dissertation.
Plagiarism Test
The Plagiarism Test must be conducted on the Dissertation before its submission to the two foreign experts.
Research Paper
Publication of at least one research paper based on the Ph.D research in an HEC-approved W or X category journal is the requirement for the award of Ph.D degree (Y in case of Social Science only).
Placements and Career Prospects
- Research and development scientist
- University Professor
- Biomedical consultant
- Biomedical entrepreneur
- Healthcare scientist
- Product development researcher
- Industrial R&D professionals
- Clinical engineer director
- Healthcare associate and analyst
BS Robotics and Intelligent Systems
BS in Robotics and Intelligent Systems at Salim Habib University is a four-year degree program designed to equip students with the essential skills and knowledge needed to excel in the rapidly evolving fields of robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and intelligent systems.
The program, meticulously designed to meet the needs of both academic and industrial careers, ensures that students emerge with and are able to experience:
Interdisciplinary Expertise: Students will learn how to integrate knowledge from Artificial Intelligence, Robotic Design, and IoT with programming skills to develop solutions for solving real-world problems.

Industry-Integrated Learning: Students will gain experiential learning through hands-on projects in collaboration with industry experts, mentorship, and networking opportunities with professionals.

High-Tech Careers: They will be able to develop marketable and entrepreneurial skills for exciting career opportunities and innovative business ideas in a rapidly growing field globally.

Program Education Objectives
PEO-1: Graduates would be competent individuals in their respective field to meet the technological challenges related to design, develop, and implement intelligent robotic systems for diverse applications.
PEO-2: Graduates would reflect moral values, ethical and professional attitude, leadership skills as well as entrepreneurial qualities.
PEO-3: Graduates would be able to engage in lifelong learning and support the global community with involvement in emerging technological research and development.
Career Prospects & Internships
Robotics Engineer: Design, build, and maintain robotic systems to enhance automation and efficiency in various industries.
AI and Machine Learning Expert/Developer: Develop intelligent algorithms that enable robots and systems to learn from data and make autonomous decisions
Data Scientist: Analyze and interpret data to improve the performance and capabilities of intelligent robotic systems.
Computer Vision Engineer: Create systems that enable robots to interpret and process visual information for navigation and interaction.
IoT and Embedded Systems Engineer: Design and integrate smart devices that communicate within the Internet of Things to support intelligent robotic systems.
Autonomous Systems Engineer: Design and develop self-operating robots and systems for applications such as autonomous vehicles and drones.
Automation Engineer: Implement automated robotic systems to enhance efficiency and productivity in industrial operations.
Tech Entrepreneur: Innovate and launch businesses focused on advanced robotics and intelligent system technologies.
Software Developer: Create software that enables robots and intelligent systems to perform complex tasks and solve real-world problems.
Smart Systems Developer: Design integrated intelligent systems that enhance the functionality and connectivity of robotic devices and environments.
Freelancer: Offer specialized services in robotics and intelligent systems, working on diverse projects across industries.
Researcher: Conduct research in robotics and intelligent systems, contributing to advancements and technological breakthroughs.
Control Systems Engineer: Design control systems that govern the behavior and performance of intelligent robotic systems.
Product Manager: Oversee the development and launch of robotics and intelligent systems products, ensuring they meet market needs and business objectives.
Technical Consultant: Provide expert advice on implementing and optimizing robotics and intelligent systems for various clients.
Field Service Engineer: Install, maintain, and repair robotic and intelligent systems, ensuring optimal performance in real-world environments.
Hands-on Learning and Innovative Projects
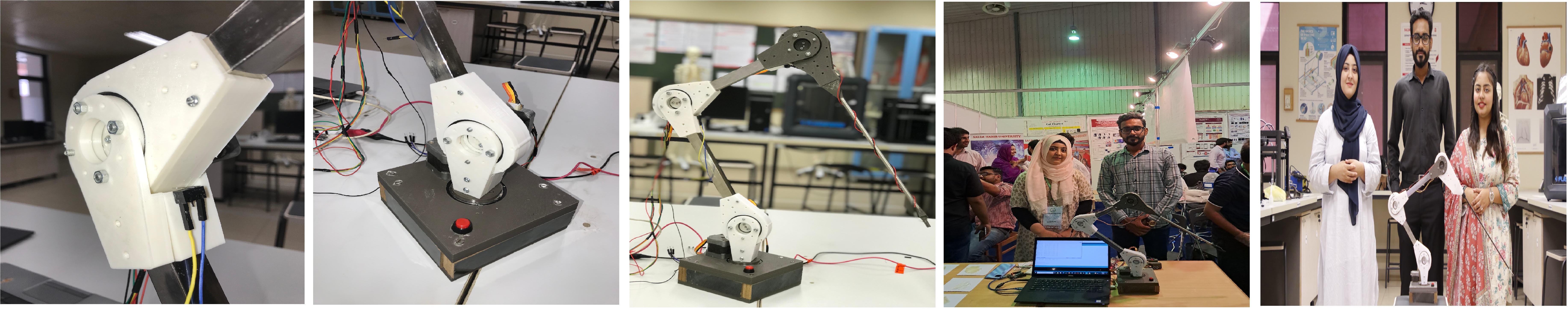 From Concept to Showcase: Students Designing, Building, and Presenting Their Innovative Project “Robotic Grasper with An Integrated Haptic Feedback Mechanism”
From Concept to Showcase: Students Designing, Building, and Presenting Their Innovative Project “Robotic Grasper with An Integrated Haptic Feedback Mechanism”
The Robotic Grasper with an Integrated Haptic Feedback Mechanism exemplifies the cutting-edge work being done within the Faculty of Engineering. Developed using our state-of-the-art in-house 3D printing facility, this project highlights the advanced capabilities of our engineering students and faculty. Leveraging on-campus 3D printing resources allows us to create highly precise and customized components, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
We are especially proud of faculty of Engineering students behind this project—Syeda Fakhra Jalal, Zarish Majid Shaikh, and Mirza Areeb Baig. Their innovative Robotic Grasper has secured 3rd place in the final round of the prestigious IEEE Region 10 Robotics Competition, one of the leading robotics challenges in the Asia-Pacific region. This achievement marks the second consecutive year that a team from SHU has secured a spot in this elite competition, underscoring our commitment to hands-on learning and technological excellence.
Scheme of Study (Semester wise)
- Duration: 4 Years
- Semesters: 8
- Credit Hours: 135
1st Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅰ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MTH 101* | Basic Mathematics | 3+0 | |
| PHC101 | Applied Physics | 2+1 | |
| IST101 | Islamic Studies/Ethical Behavious | 2+0 | |
| ENG101 | Functional English | 3+0 | |
| CSCxxx | Introduction to Information & Communication Technologies | 2+1 | |
| ELE101 | Basic Electrical Engineering | 3+1 | |
| RIS101 | Engineering Workshop | 0+1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 16 | ||
Semester - ⅠⅠ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| ICPxxx | Ideology & Constitution of Pakistan | 2+0 | |
| XXXxxx | Foreign Language | 2+0 | |
| MTH103 | Calculus & Analytical Geometry | 3+0 | |
| RIS102 | Engineering Mechanics | 2+1 | |
| CSC103 | Object Oriented Programming | 3+1 | |
| ELE103 | Electronics - I | 3+1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
2nd Year |
|||
Semester - ⅠⅠⅠ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MTH201 | Linear Algebra & Differential Equation | 3+0 | |
| CSCxxx | Data Structures & Algorithm | 2+1 | |
| ELE203 | Digital Logic Design | 3+1 | |
| BME201 | Computer Aided Engineering Drawing | 0+1 | |
| ELE204 | Electronics - II | 3+1 | |
| RIS241 | Introduction to Robotics | 2+0 | |
| XXXxxx | Occupational Health and Safety | 1+0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 18 | ||
Semester - ⅠⅤ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| XXXxxx | Civics and Community Engagement | 2+0 | |
| MTH202 | Complex Variable & Transformation | 3+0 | |
| MTH301 | Statistics | 3+0 | |
| ELE302 | Signals & Systems | 2+1 | |
| RIS221 | Microprocessor and Interfacing | 2+1 | |
| RIS242 | Robotic System & Programming | 2+1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 17 | ||
3rd Year |
|||
Semester - Ⅴ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| RIS331 | Introduction to Data Science | 2+1 | |
| RIS211 | Digital Signal Processing | 3+1 | |
| RIS212 | Control Systems | 3+1 | |
| RIS332 | Artificial Intelligence | 2+1 | |
| RIS322 | Embedded System | 2+1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 17 | ||
Semester - ⅤⅠ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| MTH302 | Numerical Analysis | 3+0 | |
| RIS313 | Digital Image Processing | 2+1 | |
| RIS333 | Introduction to Deep Learning | 2+1 | |
| RIS323 | Sensors & Actuators | 3+1 | |
| RIS343 | Robot Modeling & Control | 3+1 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 17 | ||
4th Year |
|||
Semester - ⅤⅡ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| RIS449 | Final Year Design Project I | 0+3 | |
| Expository Writing | 3+0 | ||
| RIS444 | Human-Robot Interaction | 3+1 | |
| XXXxxx | Elective I | 3+0 | |
| XXXxxx | Elective II | 3+0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 16 | ||
Semester - ⅤⅢ |
|||
| Course Code | Course Title | Credit Hours | |
| RIS449 | Final Year Design Project II | 0+3 | |
| Principles of Management and Economics | 2+0 | ||
| MGT401 | Entrepreneurship | 2+0 | |
| RIS445 | Industrial Automation | 2+1 | |
| XXXxxx | Elective III | 3+0 | |
| XXXxxx | Elective IV | 3+0 | |
| Total Credit Hours | 16 | ||
List Of Electives:
| Course Code | Course Name | CHrs | Pre-requisite |
| RIS451 | Computer Vision | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS452 | Intelligent Systems | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS453 | Pattern Recognition | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS454 | Mobile Application Development | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS455 | Artificial Intelligence for Manufacturing | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS456 | IoT & Sensors Networks | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS457 | Optimal Kinematic Design of Robots | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS458 | Artificial Neural Network | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS459 | AI for Computer Games | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS460 | Chatbots | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS461 | Biomechanics for Robotics | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS462 | Swarms and Collective Intelligence | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS463 | Medical Robotics Systems | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS464 | Biomedical Instrumentation | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS465 | Big Data Technologies | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS466 | Augmented Reality | 3 + 0 | |
| RIS467 | Natural Language Processing | 3 + 0 |
IEEE SHU Student Branch secured YP Mentoring Meet Funding
We are proud to announce that the IEEE SHU Student Branch has won a Young Professionals (YP) Mentoring Meet Fund worth USD 1000. Congratulations to Engr. Tooba Khan, Lecturer, Biomedical Engineering, and Advisor EMBS and ComSoc, Mr. M. Wasim Munir, Assistant Professor, Biomedical Engineering, and Branch Counsellor, IEEE SHU Student Branch, and the branch members whose efforts have resulted in this outstanding achievement!

IEEE SHU Student Branch secured Humanitarian Grant
The IEEE SHU Student Branch has secured a $6,690 grant from the IEEE Humanitarian Technology Board (HTB) for their project titled 'SolarVitalize: Empowering Education & Well-being with Renewable Energy in Rural Areas.’ The project, led by Mr. M. Wasim Munir, Assistant Professor, Biomedical Engineering, and Principal Investigator (PI), and Engr. Tooba Khan, Lecturer, Biomedical Engineering, and co-PI, will be implemented with the valuable contributions of IEEE SHU Student Branch members Fakhra Jalal, Amna Javed, Usama Javed, and Umer Sheikh. This initiative, supported by the IEEE Karachi Section, IEEE SHU Student Branch, and Omair Sana Welfare Foundation, supports quality education and well-being, fostering a brighter future for rural communities.
Faculty Members Elevated to Senior IEEE Members
We offer our congratulations to Prof. Dr. Zeeshan Ul Haque, Dean, Faculty of Engineering, Salim Habib University, and Mr. M. Wasim Munir, Assistant Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Salim Habib University, on being promoted to Senior IEEE Members of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), a professional association for electronics engineering, electrical engineering, and other related disciplines.

Department of Biomedical Engineering secures Erasmus+ Project BIOMED 5.0
Prof. Dr. Zeeshan Ul Haque, Dean, Faculty of Engineering, Engr. Hassan Ali, Lecturer, Department of Biomedical Engineering, and Engr. Muhammad Amir, Lecturer, Department of Biomedical Engineering, have successfully obtained a grant for the Erasmus+ Project BIOMED 5.0: Capacity Building in Biomedical Engineering Education for Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0/5.0 Technologies.
Research Publication
Faculty member from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Engr. Shaheer Mirza’s research work has been published in a Subscription-Based Elsevier Journal.
Robotics Project Selected for IEEE Region 10 Robotics Competition
Syeda Fakhra Jalal, Zarish Majid Shaikh, and Mirza Areeb Baig, Final Year Biomedical Engineering students at Salim Habib University, have earned a coveted place in the final round of the rigorous competition with their innovative project, the Robotics Grasper. The IEEE Region 10 Robotics Competition is one of the leading robotics challenges in the Asia-Pacific region, attracting the brightest minds from across the continent. We are proud of our team, and beyond proud that this marks the second consecutive year a team from SHU has secured a spot in this elite competition!

Oral Presentation in International Biomedical and Digital Health Conference 2024 held at NEDUET
The Department of Biomedical Engineering at Salim Habib University is pleased to announce that two research projects by our students were shortlisted for oral presentation at the 3rd International Biomedical and Digital Health Conference 2024, organized by NED University of Engineering & Technology (NEDUET) in collaboration with the Institution of Engineers Pakistan (IEP), held from the 24th to the 25th of April, 2024, at NEDUET, and one of these projects won Second Prize.- The Development and Characterization of Biomimetic Skin Patch for IV Insertion on Medical Simulators by Misha Aijaz, Amna Ayaz, and Usama Javed, supervised by Engr. Tooba Khan
- Self-Healing Moringa Guar Gum Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications by Fatima Siddiqui, Rosemary John, and Tariq Amin, supervised by Engr. Tooba Khan and Engr. Abdul Moiz
Among these, the research work titled ‘The Development and Characterization of Biomimetic Skin Patch for IV Insertion on Medical Simulators' was awarded second place.
Financing of FYDP’s for the year 2023-24 by PEC
We take immense pride in announcing that five Final Year Design Projects (FYDPs) created by Salim Habib University’s bright Biomedical Engineering students have been selected for financing for the year 2023-2024 by the Pakistan Engineering Council (PEC).- Design and Development of Human Patient Simulator, supervised by Prof. Dr. Zeeshan Ul Haque, Dean, Faculty of Engineering, and Engr. Tooba Khan, Lecturer Biomedical Engineering
- Fabrication of Sodium Alginate Microparticles Embedded in PVA Hydrogel for Tissue Regeneration, supervised by Mr. M. Wasim Munir, Assistant Professor Biomedical Engineering, Engr. Tooba Khan, and Engr. Abdul Moiz, Research & Teaching Associate, Biomedical Engineering
- Eco-Friendly Bioplastic/PVA Composite for Biomedical Applications, supervised by Engr. Tooba Khan and Engr. Hassan Ali, Lecturer Biomedical Engineering
- Comparative Evaluation of the Properties of PEEK, PMMA, and Titanium for Cranial Implants, supervised by Engr. Tooba Khan and Mr. M. Wasim Munir
- Hand-e-Ssist (Automated Therapeutic Arm), supervised by Engr. Hassan Ali and Engr. Tooba Khan


Dr. M. Zeeshan Ul Haque
Professor & Dean

Dr. Syed Mehmood Ali
Associate Professor & Head of Biomedical Engineering

Engr. Dr. Munsif Ali Jatoi
Associate Professor

Mr. Muhammad Wasim Munir
Assistant Professor

Dr. Irfan Ahmed Usmani
Assistant Professor

Engr. Hassan Ali
Lecturer

Ms. Madiha Imdad
Lecturer

Engr. Gul Munir
Lecturer

Engr. Tooba Khan
Lecturer

Mr. Muhammad Sayem Hanif
Lecturer

Engr. Muhammad Aamir
Lecturer

Engr. Muhammad Shaheer Mirza
Lecturer

Engr. Abdul Moiz
Lecturer